Network Scanning
This project demonstrates network scanning and reconnaissance techniques using Nmap and hping3 inside a controlled lab environment. The lab is composed of Kali Linux as the attacker machine and the OWASP Broken Web Apps VM 1.2 as the target. The goal was to simulate real-world penetration testing tasks such as host discovery, port scanning, and packet crafting, all while documenting findings and behavior across multiple test scenarios.
Scanning Demonstration
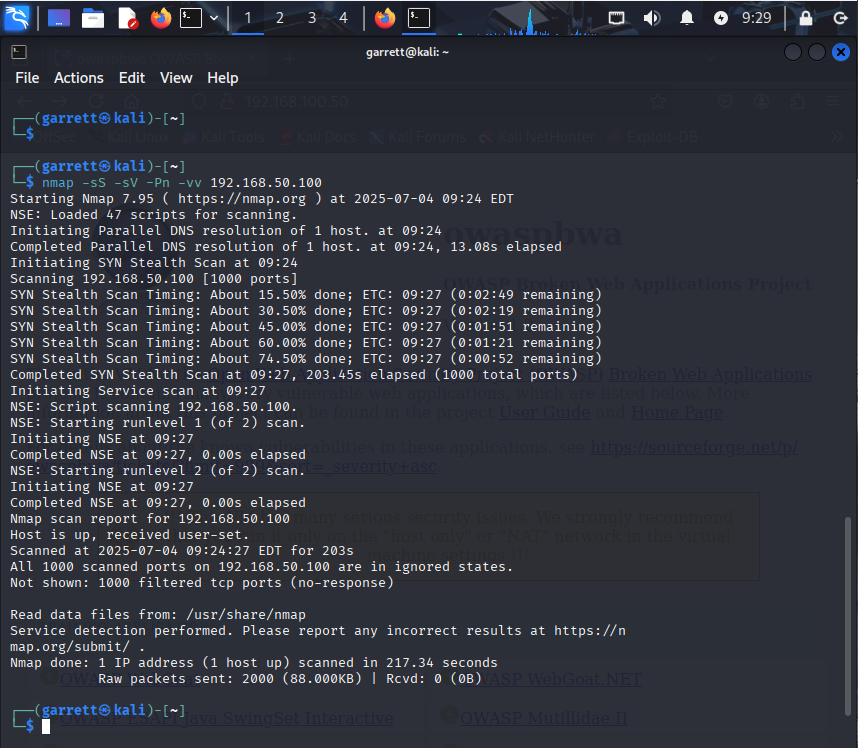
-sV service detection returned limited results due to filtered ports or firewall settings.Further enumeration used advanced flags:
-sS (stealth SYN scan), -sV (service version detection), -Pn (skip ping), and -vv (extra verbosity).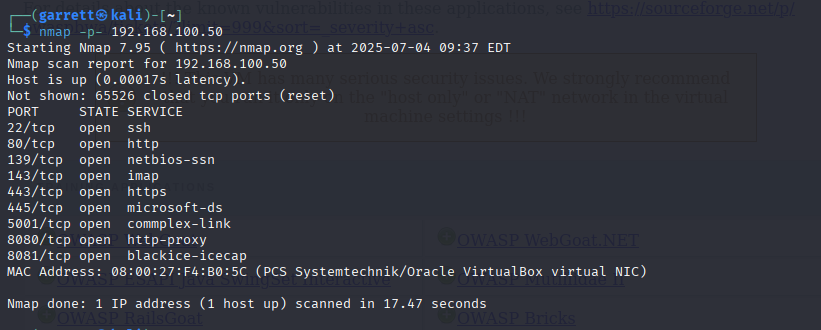
hping3 -1 192.168.100.50 to test host availability and bypass traditional ping restrictions. Useful when ICMP is blocked or filtered by default tools like ping.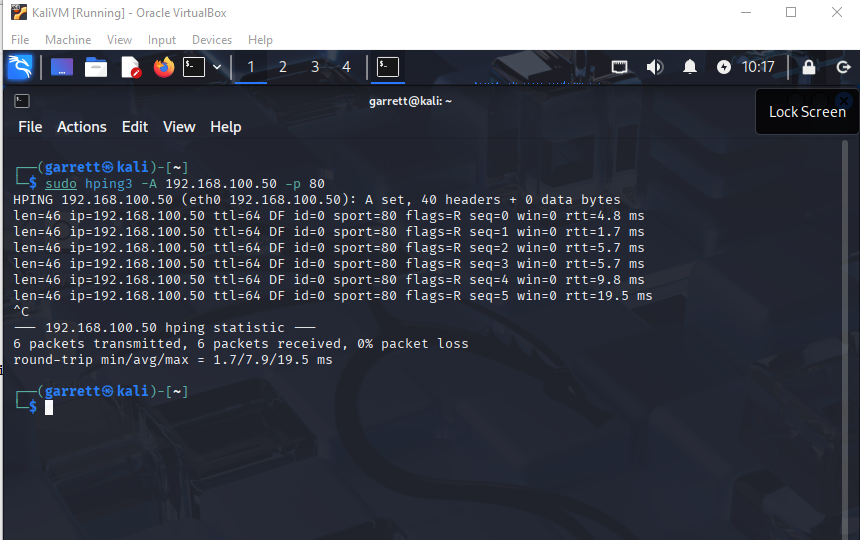
hping3 -A 192.168.100.50 -p 80 to send TCP ACK packets to port 80. This technique helps identify firewall rules by checking if the port is unfiltered (responds) or silently dropped.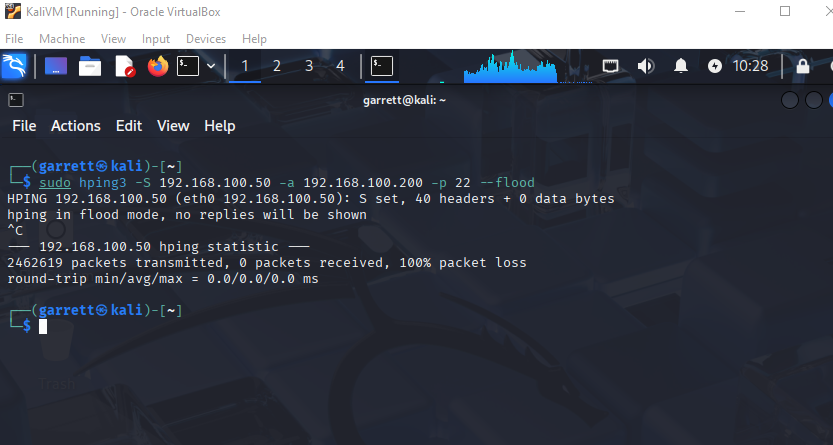
hping3 -S 192.168.100.50 -a 192.168.100.200 -p 22 --flood to overwhelm port 22 (SSH) on the target.The
-a flag spoofed the source IP, simulating a denial-of-service scenario within the lab environment.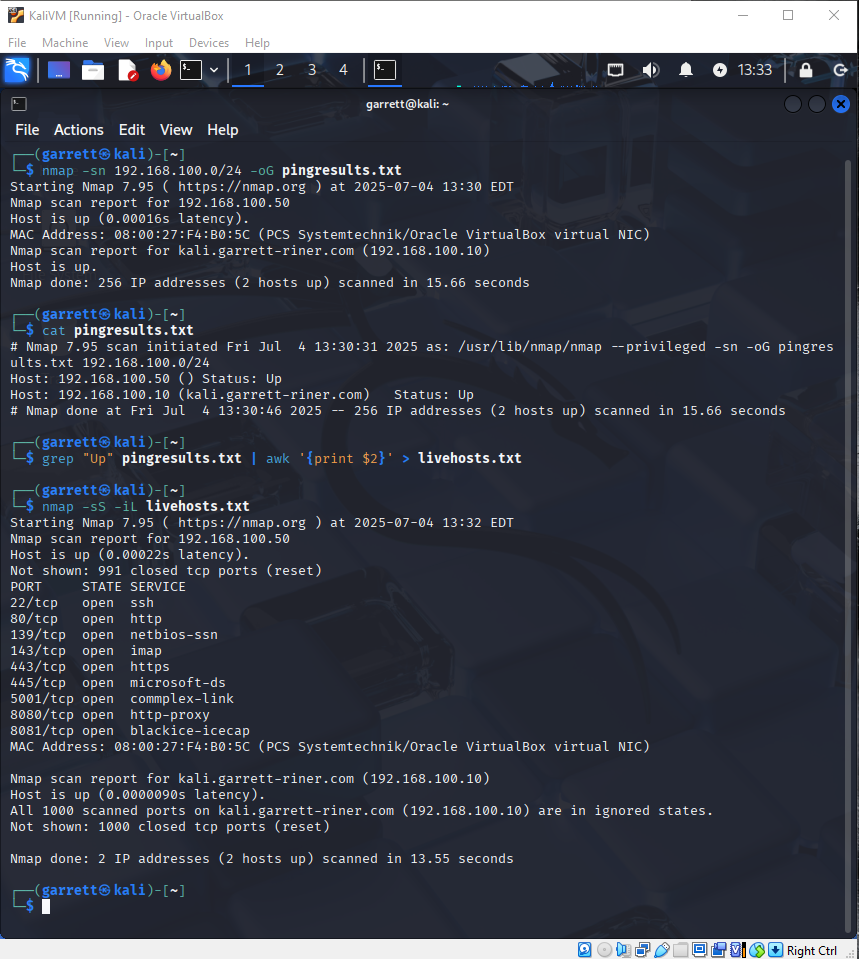
nmap -sn 192.168.100.0/24 -oG pingresults.txt to identify live hosts.Extracted responsive IPs using
grep and awk into livehosts.txt, then performed a targeted SYN scan with nmap -sS -iL livehosts.txt to enumerate open ports and services.